S1PR1
| Sfingozin-1-fosfatni receptor 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
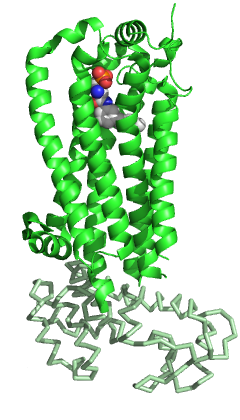 Struktura SIPR1-lizozim fuzije 3v2y[1] | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 3V2W, 3V2Y | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | S1PR1; CD363; CHEDG1; D1S3362; ECGF1; EDG-1; EDG1; S1P1 | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 601974 MGI: 1096355 HomoloGene: 1071 IUPHAR: S1P1 GeneCards: S1PR1 Gene | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 1901 | 13609 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000170989 | ENSMUSG00000045092 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P21453 | O08530 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_001400.4 | NM_007901.5 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001391.2 | NP_031927.2 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) | Chr 1: 101.7 - 101.71 Mb | Chr 3: 115.41 - 115.42 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
S1PR1 (sfingozin-1-fosfatni receptor 1, S1P1, EDG1, endotelni diferencijacioni gen 1) je protein koji je kod ljudi kodiran S1PR1 genom. S1P1 je G protein spregnuti receptor za koji se vezuje lipidni signalni molekul sfingozin-1-fosfat (S1P).
Funkcija
Ovaj protein je visoko izražen u endotelnim ćelijama. On vezuje sfingozin-1-fosfat sa visokim afinitetom i specifičnošću, i smatra se da učestvuje u procesima koji regulišu diferencijaciju endotelnih ćelija. Aktivacija ovog receptora indukuje međućelijsku adheziju.[2]
Interakcije
S1PR1 formira interakcije sa 5-HT1A receptorom,[3] GNAI1[4] i GNAI3.[4]
Vidi još
Reference
- ^ Hanson, M. A.; Roth, C. B.; Jo, E.; Griffith, M. T.; Scott, F. L.; Reinhart, G.; Desale, H.; Clemons, B.; Cahalan, S. M. (2012). „Crystal Structure of a Lipid G Protein-Coupled Receptor”. Science. 335 (6070): 851. doi:10.1126/science.1215904.
- ^ „Entrez Gene: EDG1 endothelial differentiation, sphingolipid G-protein-coupled receptor, 1”.
- ^ Salim, Kamran; Fenton Tim; et al. (2002). „Oligomerization of G-protein-coupled receptors shown by selective co-immunoprecipitation”. J. Biol. Chem. United States. 277 (18): 15482—5. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11854302. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201539200.
- ^ а б Lee, M J; Evans M; Hla T (1996). „The inducible G protein-coupled receptor edg-1 signals via the G(i)/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 271 (19): 11272—9. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8626678. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.19.11272.
Literatura
- Spiegel S (2000). „Sphingosine 1-phosphate: a ligand for the EDG-1 family of G-protein-coupled receptors.”. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 905: 54—60. PMID 10818441. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06537.x.
- Igarashi Y (2002). „[Current studies on a novel lipid mediator, sphingosine 1-phosphate, and its receptors]”. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 47 (4 Suppl): 476—9. PMID 11915345.
- Takuwa Y (2002). „[Regulation of Rho family G proteins and cell motility by the Edg family of sphingosin 1-phosphate receptors]”. Tanpakushitsu Kakusan Koso. 47 (4 Suppl): 496—502. PMID 11915348.
- Takuwa Y, Takuwa N, Sugimoto N (2003). „The Edg family G protein-coupled receptors for lysophospholipids: their signaling properties and biological activities.”. J. Biochem. 131 (6): 767—71. PMID 12038970.
- Wang D; Zhao Z; Caperell-Grant A; et al. (2008). „S1P differentially regulates migration of human ovarian cancer and human ovarian surface epithelial cells.”. Mol Cancer Ther. 7 (7): 1993—2002. PMID 18645009.
- Hla T, Maciag T (1990). „An abundant transcript induced in differentiating human endothelial cells encodes a polypeptide with structural similarities to G-protein-coupled receptors.”. J. Biol. Chem. 265 (16): 9308—13. PMID 2160972.
- Lee MJ, Evans M, Hla T (1996). „The inducible G protein-coupled receptor edg-1 signals via the G(i)/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.”. J. Biol. Chem. 271 (19): 11272—9. PMID 8626678. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.19.11272.
- Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (1997). „Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery.”. Genome Res. 6 (9): 791—806. PMID 8889548. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791.
- An S; Bleu T; Huang W; et al. (1998). „Identification of cDNAs encoding two G protein-coupled receptors for lysosphingolipids.”. FEBS Lett. 417 (3): 279—82. PMID 9409733. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01301-X.
- Lee MJ; Van Brocklyn JR; Thangada S; et al. (1998). „Sphingosine-1-phosphate as a ligand for the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1.”. Science. 279 (5356): 1552—5. PMID 9488656. doi:10.1126/science.279.5356.1552.
- Lee MJ; Thangada S; Liu CH; et al. (1998). „Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates the G-protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 as a low affinity agonist.”. J. Biol. Chem. 273 (34): 22105—12. PMID 9705355. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.34.22105.
- Ancellin N, Hla T (1999). „Differential pharmacological properties and signal transduction of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors EDG-1, EDG-3, and EDG-5.”. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (27): 18997—9002. PMID 10383399. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.27.18997.
- Windh RT; Lee MJ; Hla T; et al. (1999). „Differential coupling of the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors Edg-1, Edg-3, and H218/Edg-5 to the G(i), G(q), and G(12) families of heterotrimeric G proteins.”. J. Biol. Chem. 274 (39): 27351—8. PMID 10488065. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.39.27351.
- Lee MJ; Thangada S; Claffey KP; et al. (1999). „Vascular endothelial cell adherens junction assembly and morphogenesis induced by sphingosine-1-phosphate.”. Cell. 99 (3): 301—12. PMID 10555146. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81661-X.
- Igarashi J, Michel T (2000). „Agonist-modulated targeting of the EDG-1 receptor to plasmalemmal caveolae. eNOS activation by sphingosine 1-phosphate and the role of caveolin-1 in sphingolipid signal transduction.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (41): 32363—70. PMID 10921915. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003075200.
- Parrill AL; Wang D; Bautista DL; et al. (2001). „Identification of Edg1 receptor residues that recognize sphingosine 1-phosphate.”. J. Biol. Chem. 275 (50): 39379—84. PMID 10982820. doi:10.1074/jbc.M007680200.
- Liu Y; Wada R; Yamashita T; et al. (2000). „Edg-1, the G protein-coupled receptor for sphingosine-1-phosphate, is essential for vascular maturation.”. J. Clin. Invest. 106 (8): 951—61. PMC 314347
 . PMID 11032855. doi:10.1172/JCI10905.
. PMID 11032855. doi:10.1172/JCI10905. - Murphy WJ; Eizirik E; Johnson WE; et al. (2001). „Molecular phylogenetics and the origins of placental mammals.”. Nature. 409 (6820): 614—8. PMID 11214319. doi:10.1038/35054550.
- Hobson JP; Rosenfeldt HM; Barak LS; et al. (2001). „Role of the sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG-1 in PDGF-induced cell motility.”. Science. 291 (5509): 1800—3. PMID 11230698. doi:10.1126/science.1057559.
- Lee MJ; Thangada S; Paik JH; et al. (2001). „Akt-mediated phosphorylation of the G protein-coupled receptor EDG-1 is required for endothelial cell chemotaxis.”. Mol. Cell. 8 (3): 693—704. PMID 11583630. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00324-0.
Spoljašnje veze
- „Lysophospholipid Receptors: S1P1”. IUPHAR Database of Receptors and Ion Channels. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. Архивирано из оригинала 07. 01. 2015. г.
- Lysophospholipid+receptors на US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- п
- р
- у
| Orfan | |
|---|---|
| Drugi | Moždano specifični angiogenezni inhibitor (1, 2, 3) • Kadherin (1, 2, 3) • Kalcitonin • CALCRL • CD97 • Kortikotropin-oslobađajući hormon (1, 2) • EMR (1, 2, 3) • Glukagon (GR, GIPR, GLP1R, GLP2R) • Hormon rasta • PACAPR1 • GPR • Latrofilin (1, 2, 3, ELTD1) • Metuzalemski protein • Paratiroidni hormon (1, 2) • Sekretin • Vazoaktivni intestinalni peptid (1, 2) |
glutamat / feromon
| Ukus | |
|---|---|
| Drugi |
Frizzled / Zaglađeni
| Uvojiti | |
|---|---|
| Zaglađeni |










