Dinamin
| Dinamin GTPaza | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifikatori | |||||||||
| EC broj | 3.6.5.5 | ||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBj PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Dinamin N | |
|---|---|
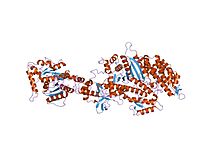 | |
| Struktura beznukleotidnog miozinskog motornog domena II iz Dictyostelium discoideum spojena sa GTPaznim domenom dinamina 1 iz Rattus norvegicus | |
| Identifikatori | |
| Simbol | Dynamin_N |
| Pfam | PF00350 |
| Pfam klan | CL0023 |
| InterPro | IPR001401 |
| PROSITE | PDOC00362 |
| Centralni region dinamina | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Struktura beznukleotidnog miozinskog motornog domena II iz Dictyostelium discoideum spojena sa GTPaznim domenom dinamina 1 iz Rattus norvegicus | |
| Identifikatori | |
| Simbol | Dynamin_M |
| Pfam | PF01031 |
| InterPro | IPR000375 |
Dinamin je GTPaza odgovorna za endocitozu u eukariotskim ćelijama. Dinamini prvenstveno učestvuju u odvajanju novoformiranih vezikula od membrane jednog ćelijskog kompartmana, i njihovom usmeravanju i spajanju sa drugim kompartmanom. Oni posreduju endocitozu sa ćelijske površine (posebno internalizaciju kaveola), kao i sa Goldžijevog aprata.[1][2][3] Dinamin učestvuje i nizu procesa deobe organela,[4] citokineze i u pružanju otpora mikrobnim patogenim.
Dinamin pripada dinaminskoj superfamiliji koja obuhvata klasične dinamine, dinaminu slične proteine, Mx proteine, OPA, mitofuzine, i GBP proteine.
Dinamin je enzim sa 96 kDa. On je privi put izolovan tokom pokušaja da se izoluju motori bazirani na mikrotubulama iz goveđeg mozga. Dinamin je intenzivno proučavan u kontekstu pupljenja klatrinom pokrivenih vezikula sa ćelijske membrane.[3][5]
Reference
- ↑ Henley, J.R., Cao, H., McNicven, M.A. (1999). “Participation of dynamin in the biogenesis of cytoplasmic vesicles”. The FASEB Journal, 13, S243-S247.
- ↑ Hinshaw, J. “Dynamin overview: The Role of Dynamin in Membrane Fission”. Arhivirano 2011-10-15 na Wayback Machine-u National institute of diabetes & digestive & kidney diseases, Laboratory of cell biochemistry and biology. accessed 021806.
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 Urrutia R., Henley J.R., Cook T., McNiven M.A. (1997). „The dynamins: Redundant or distinct functions for an expanding family of related GTPases?”. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94 (2): 377–384. DOI:10.1073/pnas.94.2.377.
- ↑ Thoms S, Erdmann R (Oct 2005). „Dynamin-related proteins and Pex11 proteins in peroxisome division and proliferation.”. FEBS J 272 (20): 5169–81. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04939.x. PMID 16218949.
- ↑ McMahon. (2004). “Researching Endocytic Mechanisms: Dynamin:. Arhivirano 2012-03-05 na Wayback Machine-u Accompaniment of Nature Reviews on Molecular Cell Biology, 5, 133-147.
Literatura
- Nicholas C. Price, Lewis Stevens (1999). Fundamentals of Enzymology: The Cell and Molecular Biology of Catalytic Proteins (Third izd.). USA: Oxford University Press. ISBN 019850229X.
- Eric J. Toone (2006). Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology, Protein Evolution (Volume 75 izd.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 0471205036.
- Branden C, Tooze J.. Introduction to Protein Structure. New York, NY: Garland Publishing. ISBN: 0-8153-2305-0.
- Irwin H. Segel. Enzyme Kinetics: Behavior and Analysis of Rapid Equilibrium and Steady-State Enzyme Systems (Book 44 izd.). Wiley Classics Library. ISBN 0471303097.
- Robert A. Copeland (2013). Evaluation of Enzyme Inhibitors in Drug Discovery: A Guide for Medicinal Chemists and Pharmacologists (2nd izd.). Wiley-Interscience. ISBN 111848813X.
- Gerhard Michal, Dietmar Schomburg (2012). Biochemical Pathways: An Atlas of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (2nd izd.). Wiley. ISBN 0470146842.
Spoljašnje veze

- MeSH Dynamins
- p
- r
- u
3.6.3 |
| ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3.6.4 |
3.6.5.1: Heterotrimerni G protein | |
|---|---|
3.6.5.2: Male GTPaze > Ras superfamilija | |
3.6.5.3: Protein-sintetišuće GTPaze | Prokariotski (IF-2, EF-Tu, EF-G) • Eukariotski |
3.6.5.5-6: Polimerizacioni motori | Dinamin • Tubulin |








