Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
| DUSP3 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
| List of PDB id codes |
|---|
1J4X, 1VHR, 3F81 |
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | DUSP3, VHR, dual specificity phosphatase 3 |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 600183; MGI: 1919599; HomoloGene: 20870; GeneCards: DUSP3; OMA:DUSP3 - orthologs |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 17 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 17q21.31 | Start | 43,766,125 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 43,778,977 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 11 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 11|11 D | Start | 101,861,969 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 101,877,839 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - Skeletal muscle tissue of rectus abdominis
- Skeletal muscle tissue of biceps brachii
- saphenous vein
- vastus lateralis muscle
- muscle of thigh
- myocardium of left ventricle
- thoracic diaphragm
- gastrocnemius muscle
- right ventricle
- apex of heart
|
| | Top expressed in | - ascending aorta
- aortic valve
- substantia nigra
- muscle of thigh
- primary visual cortex
- superior frontal gyrus
- interventricular septum
- skeletal muscle tissue
- tunica media of zone of aorta
- vastus lateralis muscle
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
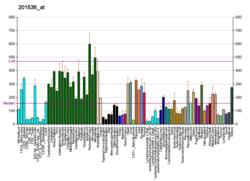
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - phosphoprotein phosphatase activity
- MAP kinase phosphatase activity
- hydrolase activity
- protein kinase binding
- protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- phosphatase activity
- protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- cytoskeletal protein binding
- receptor tyrosine kinase binding
- protein tyrosine kinase binding
| | Cellular component | - cytosol
- nucleoplasm
- immunological synapse
- nucleus
| | Biological process | - protein dephosphorylation
- positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle
- negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway
- negative regulation of JNK cascade
- negative regulation of MAPK cascade
- negative regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade
- peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation
- negative regulation of T cell activation
- in utero embryonic development
- dephosphorylation
- negative regulation of cell migration
- negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway
- negative regulation of chemotaxis
- regulation of focal adhesion assembly
- cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus
- positive regulation of focal adhesion disassembly
- peptidyl-tyrosine dephosphorylation involved in inactivation of protein kinase activity
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP3 gene.[5][6]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dual specificity protein phosphatase subfamily. These phosphatases inactivate their target kinases by dephosphorylating both the phosphoserine/threonine and phosphotyrosine residues. They negatively regulate members of the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase superfamily (MAPK/ERK, SAPK/JNK, p38), which are associated with cellular proliferation and differentiation. Different members of the family of dual specificity phosphatases show distinct substrate specificities for various MAP kinases, different tissue distribution and subcellular localization, and different modes of inducibility of their expression by extracellular stimuli. This gene maps in a region that contains the BRCA1 locus which confers susceptibility to breast and ovarian cancer. Although DUSP3 is expressed in both breast and ovarian tissues, mutation screening in breast cancer pedigrees and in sporadic tumors was negative, leading to the conclusion that this gene is not BRCA1.[6]
Interactions
DUSP3 has been shown to interact with MAPK3[7] and MAPK1.[7]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000108861 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000003518 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Folander K, Douglass J, Swanson R (Feb 1995). "Confirmation of the assignment of the gene encoding Kv1.3, a voltage-gated potassium channel (KCNA3) to the proximal short arm of human chromosome 1". Genomics. 23 (1): 295–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1500. PMID 7829094.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DUSP3 dual specificity phosphatase 3 (vaccinia virus phosphatase VH1-related)".
- ^ a b Todd, J L; Tanner K G; Denu J M (May 1999). "Extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1 and ERK2 are authentic substrates for the dual-specificity protein-tyrosine phosphatase VHR. A novel role in down-regulating the ERK pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (19). UNITED STATES: 13271–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.19.13271. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10224087.
Further reading
- Ishibashi T, Bottaro DP, Chan A, et al. (1993). "Expression cloning of a human dual-specificity phosphatase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (24): 12170–4. Bibcode:1992PNAS...8912170I. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.24.12170. PMC 50720. PMID 1281549.
- Kamb A, Futreal PA, Rosenthal J, et al. (1995). "Localization of the VHR phosphatase gene and its analysis as a candidate for BRCA1". Genomics. 23 (1): 163–7. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1473. PMID 7829067.
- Jones KA, Black DM, Brown MA, et al. (1995). "The detailed characterisation of a 400 kb cosmid walk in the BRCA1 region: identification and localisation of 10 genes including a dual-specificity phosphatase". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (11): 1927–34. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.11.1927. PMID 7874108.
- Yuvaniyama J, Denu JM, Dixon JE, Saper MA (1996). "Crystal structure of the dual specificity protein phosphatase VHR". Science. 272 (5266): 1328–31. Bibcode:1996Sci...272.1328Y. doi:10.1126/science.272.5266.1328. PMID 8650541. S2CID 33816598.
- Todd JL, Tanner KG, Denu JM (1999). "Extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) 1 and ERK2 are authentic substrates for the dual-specificity protein-tyrosine phosphatase VHR. A novel role in down-regulating the ERK pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (19): 13271–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.19.13271. PMID 10224087.
- Alonso A, Saxena M, Williams S, Mustelin T (2001). "Inhibitory role for dual specificity phosphatase VHR in T cell antigen receptor and CD28-induced Erk and Jnk activation". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (7): 4766–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006497200. PMID 11085983.
- Najarro P, Traktman P, Lewis JA (2001). "Vaccinia virus blocks gamma interferon signal transduction: viral VH1 phosphatase reverses Stat1 activation". J. Virol. 75 (7): 3185–96. doi:10.1128/JVI.75.7.3185-3196.2001. PMC 114112. PMID 11238845.
- Alonso A, Rahmouni S, Williams S, et al. (2003). "Tyrosine phosphorylation of VHR phosphatase by ZAP-70". Nat. Immunol. 4 (1): 44–8. doi:10.1038/ni856. PMID 12447358. S2CID 10205773.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Kim HS, Song MC, Kwak IH, et al. (2003). "Constitutive induction of p-Erk1/2 accompanied by reduced activities of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A and MKP3 due to reactive oxygen species during cellular senescence". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (39): 37497–510. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211739200. PMID 12840032. S2CID 7806506.
- Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs". Nat. Genet. 36 (1): 40–5. doi:10.1038/ng1285. PMID 14702039.
- Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The status, quality, and expansion of the NIH full-length cDNA project: the Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)". Genome Res. 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi:10.1101/gr.2596504. PMC 528928. PMID 15489334.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Rahmouni S, Cerignoli F, Alonso A, et al. (2006). "Loss of the VHR dual-specific phosphatase causes cell-cycle arrest and senescence". Nat. Cell Biol. 8 (5): 524–31. doi:10.1038/ncb1398. PMID 16604064. S2CID 20976640.
- Hao L, ElShamy WM (2007). "BRCA1-IRIS activates cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer cells by downregulating the JNK phosphatase DUSP3/VHR". Int. J. Cancer. 121 (1): 39–46. doi:10.1002/ijc.22597. PMID 17278098. S2CID 24555741.
- Hoyt R, Zhu W, Cerignoli F, et al. (2007). "Cutting edge: selective tyrosine dephosphorylation of interferon-activated nuclear STAT5 by the VHR phosphatase". J. Immunol. 179 (6): 3402–6. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.179.6.3402. PMC 2770724. PMID 17785772.

 1j4x: HUMAN VH1-RELATED DUAL-SPECIFICITY PHOSPHATASE C124S MUTANT-PEPTIDE COMPLEX
1j4x: HUMAN VH1-RELATED DUAL-SPECIFICITY PHOSPHATASE C124S MUTANT-PEPTIDE COMPLEX 1vhr: HUMAN VH1-RELATED DUAL-SPECIFICITY PHOSPHATASE
1vhr: HUMAN VH1-RELATED DUAL-SPECIFICITY PHOSPHATASE






















